SNMP Enumeration
SNMP-Check command
Snmp-check is a great tool for getting more information about snmp
snmp-check 192.168.150.42 -c publicSNMP-Walk Enumeration
snmpwalk tool
snmpwalk -v2c -c internal 10.10.11.193snmpbulkwalk ( a much faster walk tool)
snmpbulkwalk -v2c -c internal 10.10.11.193SNMP Password cracking
onesixtyone tool
onesixtyone 192.168.185.149 -c /usr/share/doc/onesixtyone/dict.txtOr (using the SecLists dictionary, the one used in AutoRecon)
onesixtyone 192.168.185.149 -c /usr/share/seclists/Discovery/SNMP/common-snmp-community-strings-onesixtyone.txtsnmpbrute tool (for snmp-v2 bruteforce)
When we need to brute force snmpv2 not the v1, we can either use hydra with snmp2://ip_add or snmpbrute.py
snmpbrute -t mentorquotes.htbSNMP mibs config
in the snmp config, we need to install and enable mibs to get a readable output
install the mibs
sudo apt-get install snmp-mibs-downloader
sudo download-mibsadjust the snmp config, to comment the mibs line
#/etc/snmp/snmp.conf
#mibs :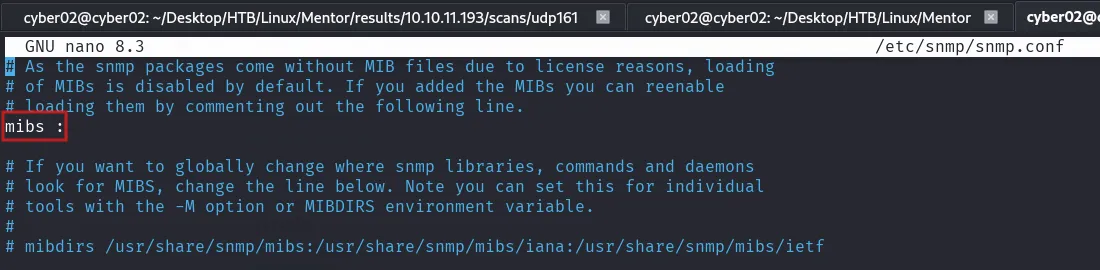
SNMP Extended queries
Check for extended queries
if the regular snmpwalk gave nothing interesting, we can check the extended queries
snmpwalk -v 1 -c public 192.168.185.149 NET-SNMP-EXTEND-MIB::nsExtendOutputFullView specific queries
if we are interested in some queries that we want to check it alone, we use snmpget along with the specific query name. (this is usually not necessary as snmpwalk will show all extended queries values)
snmpget -v1 -c public 192.168.185.149 NET-SNMP-EXTEND-MIB::nsExtendOutputFull.\"RESET\"SNMP Specific command line argument
we need to have the snmp-mibs-downloader downloaded
sudo apt-get install snmp-mibs-downloadercomment out the only uncommented line in /etc/snmp/snmp.conf to use the mibs
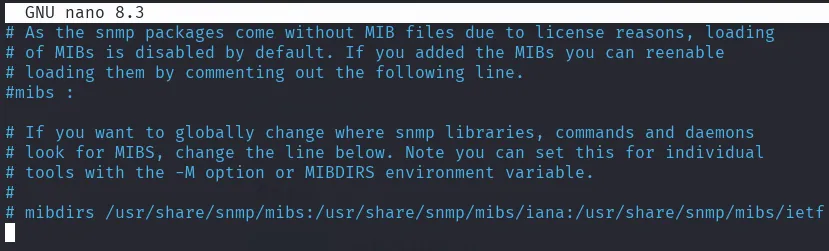
#mibs :
mibs +ALL⚙️ So in summary:
| Configuration | Behavior |
|---|---|
mibs : | Disable MIB loading (numeric OIDs only). |
#mibs : (commented) | Default → Load all available MIBs (same as mibs +ALL). |
mibs +ALL | Explicitly tell SNMP to load all MIBs (same effect, but guaranteed). |
SNMP query that retrieves the command-line arguments (parameters) of all processes running on a remote device.
snmpwalk -v 1 -c public 192.168.4.2 hrSWRunParametersHere’s the breakdown:
| Part | Meaning |
|---|---|
snmpwalk | SNMP tool that walks through a subtree of the MIB, retrieving all related values. |
-v 1 | Use SNMP version 1 protocol. |
-c public | Use community string public (like a password for SNMP v1/v2). |
192.168.4.2 | The target IP address (device you’re querying). |
hrSWRunParameters | MIB object that refers to the “Host Resources MIB”, specifically the parameters/arguments used to start each running software process. |
🔍 What you get back
The output lists entries like:
HOST-RESOURCES-MIB::hrSWRunParameters.1234 = STRING: "-l -f /etc/syslog.conf"
HOST-RESOURCES-MIB::hrSWRunParameters.5678 = STRING: "/usr/bin/python3 /opt/server.py"Each .1234 or .5678 is a process ID, and the string shows the arguments that process was started with.
Combined with hrSWRunName, it gives the full command line:
snmpwalk -v 1 -c public 192.168.4.2 hrSWRunName
We can list both process names and their parameters together using SNMP, so you can see what’s running and with what arguments on the remote host.
Run these two SNMP walks:
snmpwalk -v 1 -c public 192.168.4.2 hrSWRunName
snmpwalk -v 1 -c public 192.168.4.2 hrSWRunParameters